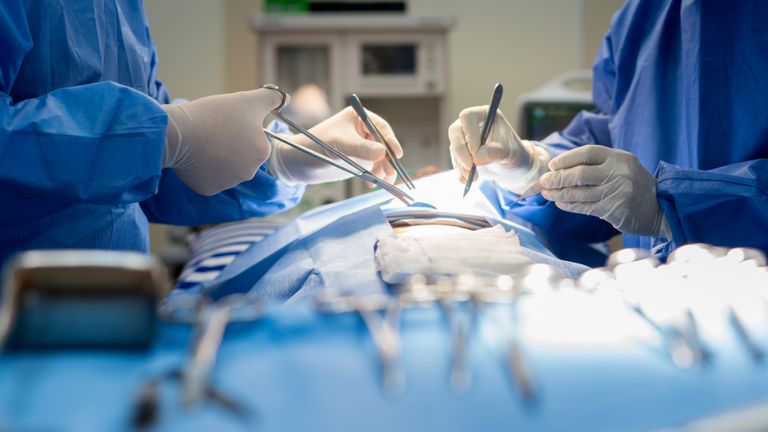
A number of patients who were diagnosed with complete paralysis have been given new hope, after pioneering nerve surgery restored movement in their elbows and hands.
Australian surgeons were able to attach nerves connected to working muscles above the spinal injury, to nerves attached to the paralysed muscle below it.
The working nerves were then able to "reanimate" the previously paralysed muscle in people with tetraplegia, which is the paralysis of the upper and lower limbs.
Young adults were able to reach their arm out, open and close their hand and pick up objects after two years of physical therapy.
It means they can now feed themselves, brush their teeth, write, use make up and handle tools.
Advertisement
The study, which has been published in The Lancet, is the largest of its kind and researchers have called it a "major advance" in restoring hand and arm function.
So far 59 nerve transfers have been made in 16 people, who had an average age of 27.
More from Australia
They had suffered spinal cord damage to the neck less than 18 months prior to the surgery, in accidents that mostly involved sport or traffic.
For 10 of the people, they combined surgery and tendon transfers, with differing styles of reconstruction bringing specific strengths to each hand.
Nerve transfers result in more natural and precise movement, whilst tendon transfers help restore power and strength.
Dr Natasha van Zyl from Austin Health in Melbourne, who led the research, said: "For people with tetraplegia, improvement in hand function is the single most important goal.
"We believe that nerve transfer surgery offers an exciting new option, offering individuals with paralysis the possibility of regaining arm and hand functions to perform everyday tasks, and giving them greater independence and the ability to participate more easily in family and work life.
"What's more, we have shown that nerve transfers can be successfully combined with traditional tendon transfer techniques to maximise benefits.
"When grasp and pinch was restored using nerve transfers in one hand and tendon transfers in the otheRead More – Source
[contf] [contfnew] 
Sky News
[contfnewc] [contfnewc]



![Taylor Swift Talks About Her Throwback To Country Roots [VIDEO]](https://amsterdamtimes.info/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/Taylor_Swift-1-e1521050909803-1-300x194.jpg)



